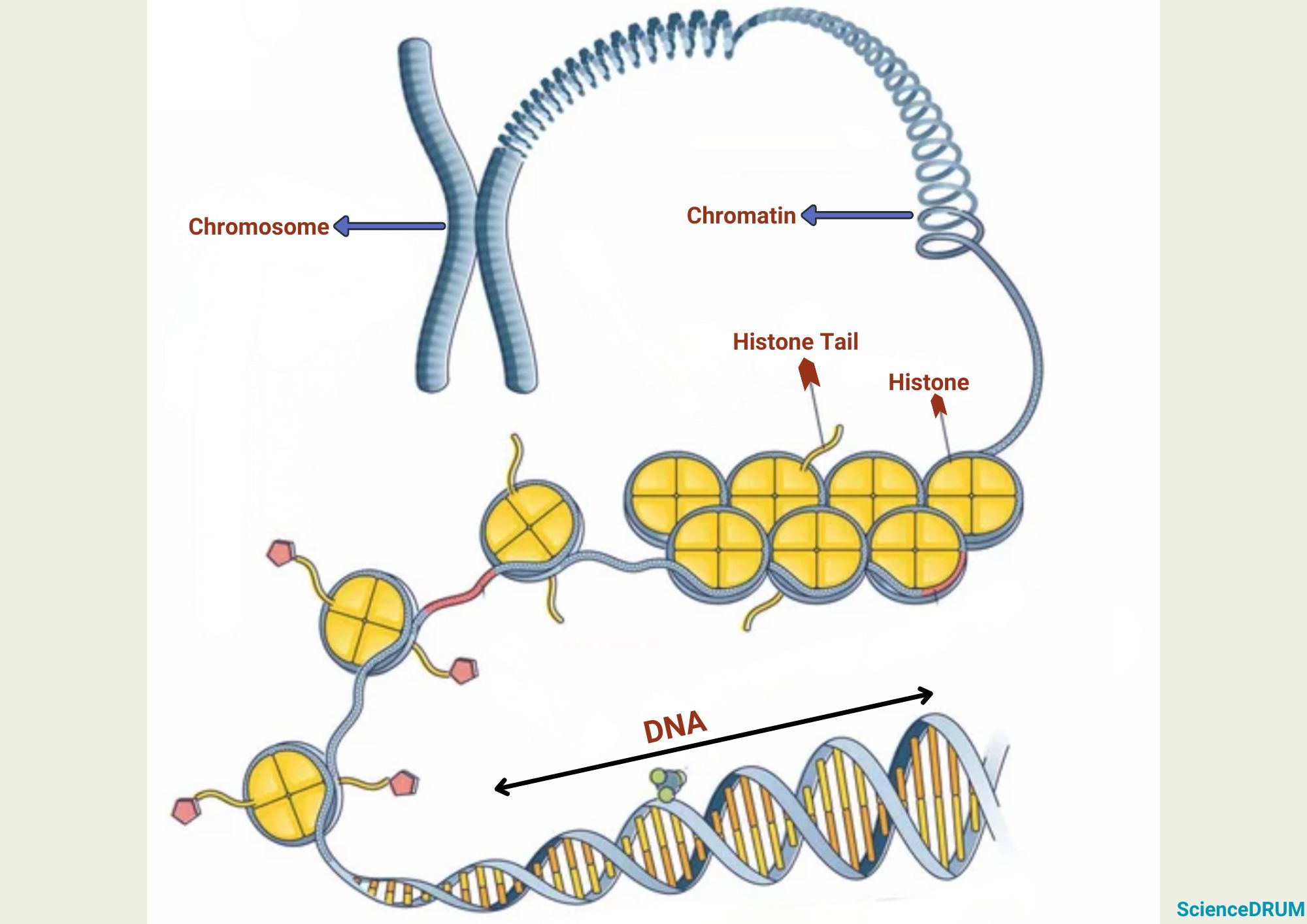
The main difference between chromatin and chromosomes is their structure and organization. Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that is more spread out and less visible under a microscope.
Chromosomes, on the other hand, are condensed and visible under a microscope. Another difference between chromatin and chromosomes is their function. Chromatin plays a role in gene expression, while chromosomes are responsible for carrying forward the genetic information and ensuring proper cell division.
This article explains the relationship between chromatin and chromosomes in detail and how their functions differ from one another.
Structure and Function of Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that make up the genetic material in our cells. DNA is a long, thin molecule that carries the genetic information which determines individual characteristics and traits.
The proteins in the chromatin structure — called histones — help package and organize the DNA. The DNA and histones form a structure called a nucleosome. Nucleosomes are the basic units of chromatin and are connected by linker DNA.
Chromatin plays a crucial role in gene expression, which is the process by which information from our genes is used to make proteins. The structure of chromatin can affect whether a gene is turned on or off, and this can have important consequences for our health. For example, changes in chromatin structure can lead to the development of cancer.
Note that chromatin, chromatids and chromosomes are exclusive structures with specific functions.
Structure and Function of Chromosomes
While chromosomes also contain the same two chemical components, their functions differ significantly from that of chromatin. Chromosomes, found in the nucleus of the cells, are responsible for carrying our genetic information.
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. The DNA strands in chromosomes are organized into regions called genes, which are responsible for making proteins. A vital point to remember here is that prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes differ in their structure.
Chromosomes also contain other types of proteins that help with the organization and function of the DNA. One of the most important functions of chromosomes is to ensure that our cells divide properly.
When a cell divides, the chromosomes are duplicated, and each new cell gets a complete set of chromosomes. This process is essential for growth and development, and any errors can lead to serious health problems.
What Is the Difference Between Chromatin and Chromosomes?

The main difference between chromatin and chromosomes is the level of compaction. Chromatin is the loose, uncondensed form of DNA that exists in the nucleus of our cells during interphase, when the cell is not dividing. Chromosomes are the highly condensed form of DNA. Chromosomes become visible during mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division.
During interphase, the cell cycle phase when the cell is not actively dividing, chromatin is loosely packed and spread throughout the nucleus. This allows for the expression of genes, as the proteins involved in gene expression can easily access the DNA.
However, when the cell enters mitosis, the chromatin is compacted into chromosomes so that they can be easily separated and distributed to daughter cells during cell division.
Chromatin is the raw material that chromosomes are made of, and its structure and composition play a crucial role in regulating gene expression and DNA replication. Another important difference between chromatin and chromosomes is their function.
Chromatin is the form of DNA that is actively involved in gene expression, DNA repair, and other cellular processes that require access to the genetic code.
Chromosomes, on the other hand, are primarily involved in cell division and the distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. It’s important to note that chromatin and chromosomes are not fixed structures, but rather dynamic and flexible entities that can change their shape and function depending on the cellular context.
For example, chromatin can be modified by chemical tags that alter its accessibility and activity, while chromosomes can undergo various stages of condensation and decondensation during cell division.
Chromatin vs. Chromosomes: Which Is More Important?
Both chromatin and chromosomes are important for our health and survival. Without chromatin, our DNA would be disorganized and difficult to access, making it impossible to carry out the processes that keep us alive. And without chromosomes, our cells would not be able to divide properly, which could lead to serious health problems.
Understanding the Difference Between Chromatin and Chromosomes
Understanding the difference between chromatin and chromosomes is important because it helps us know how our DNA works and how it can go wrong. By studying chromatin and chromosomes, scientists can gain insights into the causes of genetic diseases and develop new treatments.
Sources
1 – Cooper, G. M.: The Cell, A Molecular Approach.