Sperm cells have 23 chromosomes. During the process of meiosis, which is the specialized cell division that produces sperm cells, the number of chromosomes is halved. This means that each sperm cell contains only one set of chromosomes, rather than the usual two sets found in other cells of the body.
In this article, we will explore the basic structure of sperm cells, unique characteristics, and factors that can affect the number of chromosomes in sperm cells.
- What Are Sperm Cells?
- The Structure of Sperm Cells
- How Many Chromosomes Are There in a Sperm Cell?
- Why Do Sperm Cells Only Have 23 Chromosomes?
- Does Every Sperm Have 23 Chromosomes?
- How Many Chromosomes Are In An Egg Cell?
- The Role of Sperm Cells in Fertilization
- Factors Affecting the Number of Chromosomes in Sperm Cells
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Sperm Cells?
Sperm cells are reproductive cells or gametes that are responsible for fertilizing the female egg cell to create a new organism. They are produced by the male testes through a process called spermatogenesis, which involves the division and differentiation of germ cells.
Sperm cells are small and have a characteristic tail that enables them to swim towards the female egg. The head of a sperm cell contains genetic material in the form of chromosomes, which combine with the genetic material of the female egg to create a new individual with a unique set of traits.
Sperm cells have a limited lifespan and must fertilize the egg within a certain time frame after ejaculation to successfully result in pregnancy. Sperm cells are haploid, which means that they contain only one set of chromosomes, as opposed to the diploid cells in the body that have two sets of chromosomes.
The Structure of Sperm Cells
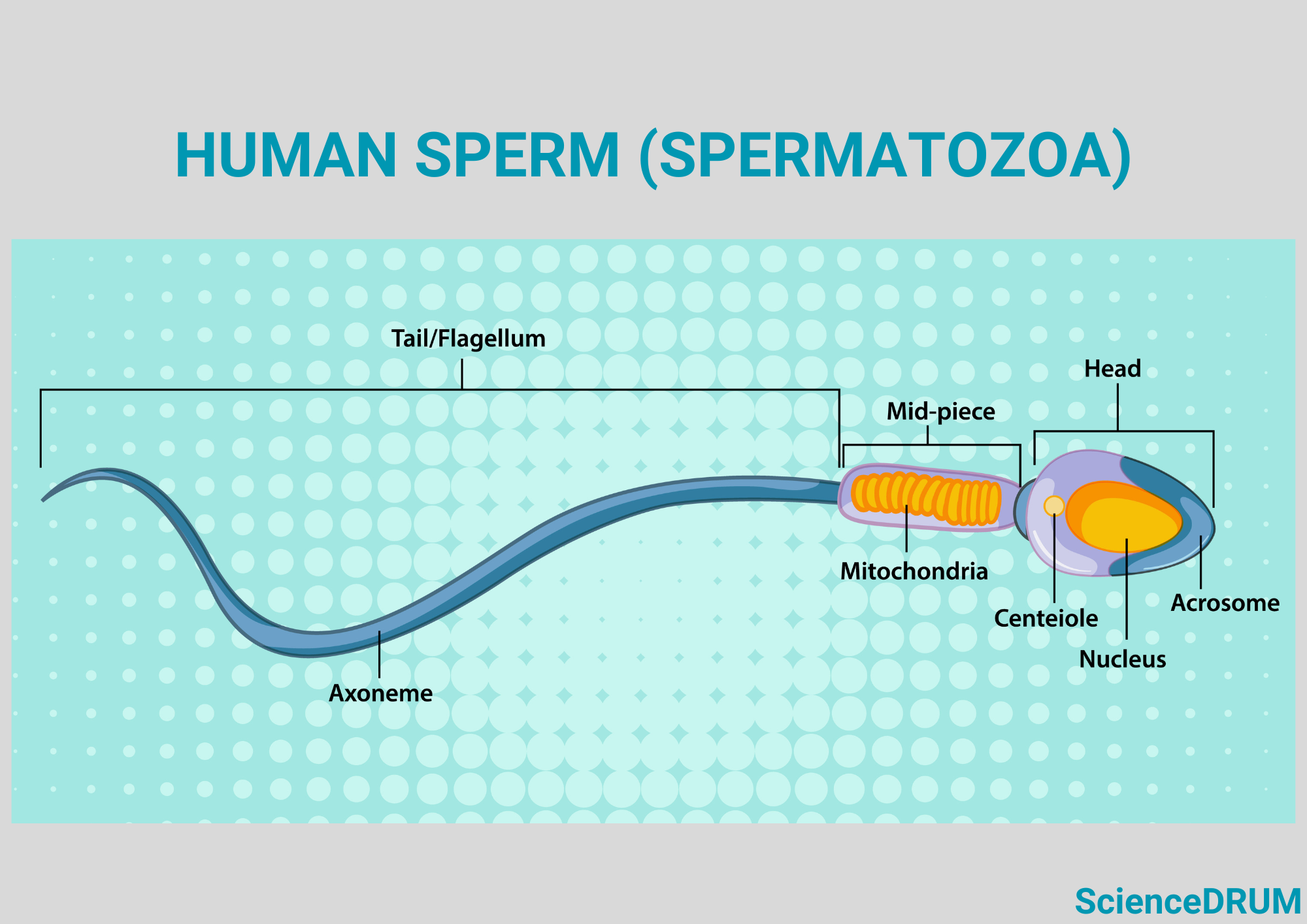
Sperm cells have a unique structure that allows them to move and fertilize an egg. They consist of three main parts — the head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the genetic material, including the chromosomes, which are tightly packed together.
The midpiece contains energy-producing mitochondria, which provide the energy needed for the sperm to move. The tail, or flagellum, propels the sperm forward and allows it to swim towards the egg.
This movement is aided by enzymes that are released by the sperm cells, which help to break down the outer layer of the female egg to allow for fertilization to occur. Factors such as age, lifestyle, and environmental factors can affect the quality and quantity of sperm cells produced.
How Many Chromosomes Are There in a Sperm Cell?
Unlike most cells in the human body, sperm cells only have 23 chromosomes, rather than the usual 46. This is because during the process of meiosis, which is the specialized cell division that produces sperm cells, the number of chromosomes is halved. This means that each sperm cell contains only one set of chromosomes, rather than the usual two sets found in other cells of the body.
Why Do Sperm Cells Only Have 23 Chromosomes?
Unlike somatic cells and zygotes, sperm cells only have 23 chromosomes. This is due to the process of meiosis, a type of cell division that results in the formation of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This results in genetic variation or diversity in the daughter cells. In the case of sperm cells, meiosis produces four haploid cells, each with 23 chromosomes.
These cells then mature into sperm cells that are capable of fertilizing an egg. When a sperm cell fertilizes an egg, the resulting zygote has a complete set of 46 chromosomes, half from the father and half from the mother.
Does Every Sperm Have 23 Chromosomes?
While all sperm cells have 23 chromosomes, not all sperm cells are the same. Sperm cells are continuously produced in the testes throughout a man’s life, and each sperm cell contains a unique combination of genetic material.
This is due to the random assortment of chromosomes during meiosis and the process of crossing over (or recombination). As a result, every sperm cell has a different set of genetic material, leading to a diverse population of sperm cells.
How Many Chromosomes Are In An Egg Cell?
Egg cells, also known as ova, are the female gametes that are responsible for fertilization in sexual reproduction. Like sperm cells, egg cells are also haploid cells, meaning they have only one set of chromosomes.
However, egg cells have a larger size than sperm cells and contain more cytoplasm, which provides nutrients and energy to the developing embryo. In humans, an egg cell has 23 chromosomes, which is half the number of chromosomes found in other cells in the body.
During fertilization, the egg cell and sperm cell combine to form a zygote with a complete set of 46 chromosomes.
The Role of Sperm Cells in Fertilization
Sperm cells play a vital role in fertilization, as they are responsible for delivering the male genetic material to the female egg cell. During sexual intercourse, sperm cells are released from the penis and travel through the female reproductive system to the fallopian tubes, where they can fertilize an egg.
The process of fertilization involves the fusion of the sperm cell and egg cell, which combines their genetic material to form a zygote. The zygote then begins to divide and develop into an embryo, which eventually grows into a new individual.
Factors Affecting the Number of Chromosomes in Sperm Cells
The number of chromosomes in sperm cells is a critical factor in determining the genetic makeup of offspring. Sperm cells normally contain 23 chromosomes, each of which carries genetic information that is necessary for the development and functioning of the organism.
However, several factors can affect the number of chromosomes in sperm cells.
- Chromosomal abnormalities. Abnormalities in chromosomes can occur during the process of sperm cell production. These abnormalities can result in changes to the number or structure of chromosomes, leading to an incorrect number of chromosomes in the sperm cell. This can result in genetic disorders or developmental abnormalities in the offspring.
- Environmental factors. Another factor that can affect the number of chromosomes in sperm cells is exposure to environmental toxins. Chemicals such as pesticides, industrial chemicals, and heavy metals can damage the DNA in sperm cells, leading to chromosomal abnormalities and changes in the number of chromosomes.
- Lifestyle factors. Habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use can also affect the number of chromosomes in sperm cells.
- Age. Age is also an important factor in the number of chromosomes in sperm cells. As men age, the number and quality of sperm cells can decline, leading to an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities and changes in the number of chromosomes. This can result in an increased risk of genetic disorders and developmental abnormalities in offspring.
- Medical conditions. Medical conditions can also affect the number of chromosomes in sperm cells. For example, certain genetic disorders can affect the process of sperm cell production, leading to changes in the number or structure of chromosomes in the sperm cells. Additionally, infections and certain medications can affect sperm cell production, leading to changes in the number of chromosomes in the sperm cells. {2}
Frequently Asked Questions
Sources
1 – Nature: “‘Semi-identical’ twins discovered.”
2 – Stanford Children: “Medical Genetics: How Chromosome Abnormalities Happen.”