
Chromosomes are located inside the cell nucleus. The nucleus is the command center that operates cell functions. Chromosomes inside the nucleus are protected by a membrane which separates it from the rest of the cytoplasm, a type of fluid found inside every cell.
This article answers vital questions about the structure of chromosomes and why its location holds special significance.
The Structure of Chromosomes
Chromosomes are tiny structures, made up of long strands of DNA that are coiled up tightly and hold all the instructions for how our bodies work. Chromosomes are vital as they dictate growth and development and can even affect our health.
They have a distinct shape, usually looking like an X or a pair of scissors. The DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones, which help compact the DNA into a manageable shape.
Where Are Chromosomes Located?
Humans have 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs of them. Each chromosome is a long, coiled-up strand of DNA, packed with genes that carry instructions for building and maintaining our body. So, where are chromosomes located? The answer is — inside the nucleus of our cells. {1}
The nucleus is the command center of the cell, surrounded by a membrane that separates it from the cytoplasm, the fluid that fills the cell. The chromosomes are carefully arranged inside the nucleus, where they can be protected and regulated by various molecular mechanisms.
Where Are Chromosomes Located in Prokaryotic Cells?
Prokaryotic cells are simple cells without a nucleus. They usually have just one circular chromosome that floats freely in the cell’s cytoplasm. This chromosome contains all the genetic information needed for the cell to survive and reproduce.
Where Are Chromosomes Located in Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells are more complex cells that have a nucleus, which acts as a control center for the cell. Eukaryotic cells typically have more chromosomes than prokaryotic cells. Humans have 46 chromosomes, for example, and plants and animals can have many more. These chromosomes are located in the nucleus of the cell.
What Is the Importance of Chromosome Location?
Chromosome location is crucial for proper cellular function as it determines which genes are accessible for transcription and which are not. The position of a chromosome within the nucleus can affect its accessibility to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins, which can influence gene expression.
The organization of chromosomes within the nucleus also plays a critical role in regulating gene expression patterns. Chromosome territories, or the specific regions within the nucleus where individual chromosomes are located, can impact gene expression through interactions between neighboring chromosomes.
Furthermore, changes in chromosome location and organization have been implicated in the development and progression of diseases such as cancer. Alterations in chromosome location can result in abnormal gene expression patterns, leading to irregular cell growth and division.
Studying chromosome location and its impact on gene expression is crucial to understand basic cellular processes such as development and differentiation, as well as disease progression. Advances in imaging technology and genome mapping have led to increased understanding of the role of chromosome location in these processes, opening up new avenues for research and potential therapeutic interventions.
The Role of the Nucleus in Chromosomal Functions
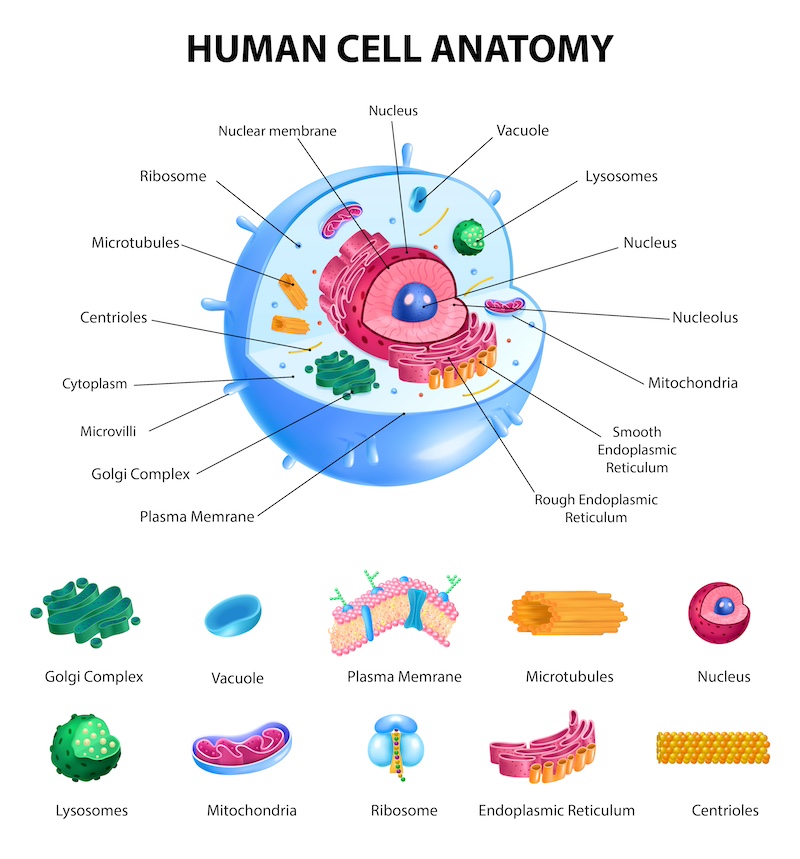
The nucleus is a critical component of the eukaryotic cell that plays a vital role in chromosome location. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope, which separates the nuclear contents from the cytoplasm.
The interior of the nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm, which contains the genetic material of the cell. The genetic material is organized into structures called chromosomes, which are made up of DNA molecules.
The nucleus plays a critical role in chromosome location by organizing the genetic material into discrete structures and positioning those structures within the nucleus. The nucleus, by organizing the genetic material, also plays a vital role in gene expression.
What Is Chromosome Packaging?
Chromosome packaging is the process by which DNA is tightly coiled around proteins called histones to form a structure known as a nucleosome. Nucleosomes play a critical role in the organization and compaction of genetic material within the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
The DNA molecule is a long, thin strand, and without packaging, it would be too large to fit inside the nucleus. Chromosome packaging allows for the DNA to be condensed into a compact, organized structure that can fit within the limited space of the nucleus.
The packaging of chromosomes also helps regulate gene expression. The way DNA is coiled around the histones can affect the accessibility of the DNA to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins that control gene expression.
Changes in chromosome packaging can alter gene expression patterns and contribute to the development of diseases such as cancer. {2}
Genes and Chromosomes
DNA, genes, and chromosomes are intrinsically linked. Each chromosome contains multiple genes. Genes are a collection of DNA molecules that encode the information to build specific proteins. The genes and chromosomes are located inside the nucleus of the cell.
The genes are situated on specific regions of the chromosome, and the number and position of the genes vary among the different chromosomes. The human genome — the complete set of genes that carry an individual’s genetic information — contains approximately 20,000-25,000 genes, all packed inside the nucleus of every cell.
Although humans have 46 chromosomes, we inherit one set of 23 chromosomes from each parent. So, where are these 23 chromosomes stored in our cells? The answer is — still inside the nucleus.
During cell division, the pairs of chromosomes split and segregate into two daughter cells, each containing one set of 23 chromosomes. This process, called meiosis, is crucial for sexual reproduction, as it creates genetically diverse offspring with a unique combination of traits from both parents.
Chromosomes in Different Types of Cells
Although chromosomes are located inside the nucleus of our cells, the next obvious question is — where and how are chromosomes found in different types of cells?
The number and arrangement of chromosomes varies among different cell types and depends on their specific function and developmental stage. For example, in a human sperm or egg cell, there are only 23 chromosomes, whereas in a skin cell, there are 46 chromosomes.
Chromosomes become visible under the microscope during cell division, forming characteristic shapes and patterns that help scientists study their behavior and structure.
Chromosomes Are Located in the Nucleus
To recap, chromosomes are located in the nucleus of our cells. And if you’re wondering whether there are chromosomes in every cell, the answer is yes. This is because chromosomes are the carriers of our genetic information, and regulate several functions essential for our development, health, and evolution.
Sources
1 – MedlinePlus: “What is a chromosome?”
2 – Los Alamos National Laboratory: “Unraveling the Chromosome.”